Hey there, reader. Picture this: a few years back, I was helping a buddy revamp his small retail shop. We were drowning in stock checks, miscounts, and frustrated customers hunting for sizes that weren’t there. That’s when I first dove into computer vision tech—it felt like magic, with cameras spotting empty shelves faster than we ever could. Fast forward, and I’ve seen this stuff transform businesses firsthand, from farms to factories. In this article, we’ll unpack the six top ways computer vision is shaking up the business world. It’s not just hype; it’s real tools driving efficiency and profits. Let’s jump in.
What is Computer Vision?
Computer vision is basically teaching machines to “see” and understand images or videos like we do, but way faster and without getting tired. It uses AI algorithms to process visual data, spotting patterns, objects, or even emotions. Think of it as the eyes of modern tech, powering everything from your phone’s face unlock to advanced industrial systems.
In business, it’s a game-changer because it automates tasks that used to rely on human eyes, cutting errors and costs. I’ve tinkered with open-source libraries like OpenCV in my own projects, and it’s wild how it turns raw pixels into actionable insights. No wonder the market’s exploding—projections show it hitting $50 billion by 2030.
Why Businesses Are Adopting Computer Vision
Remember that retail mess I mentioned? That’s why adoption’s skyrocketing—businesses crave speed and accuracy in a competitive world. Computer vision slashes manual labor, boosts safety, and opens new revenue streams. It’s not just for tech giants; even small ops can plug in affordable cameras and software.
From my experience consulting for startups, the ROI comes quick, like reducing waste in manufacturing by 20-30%. But it’s not plug-and-play; you need solid data and integration. Tools like Google’s Vision AI make it accessible, though.
The 6 Top Business Applications
Diving into specifics, these applications span industries, each solving pain points I’ve encountered or heard about from peers. We’ll break them down with examples, pros, cons, and tips on getting started.
1. Retail Inventory Management
In retail, computer vision scans shelves in real-time, tracking stock levels and alerting staff to restock. It’s like having an eagle-eyed assistant that never blinks. Amazon Go stores use this to enable cashier-less shopping, where cameras detect what you grab.
I once helped a local boutique implement a simple camera setup—it cut their inventory errors by half, freeing up time for customer chats. The tech identifies misplaced items too, keeping aisles tidy.

Unleashing Power of Computer Vision in Inventory Management
Pros:
- Reduces out-of-stock incidents by up to 25%.
- Speeds up audits from hours to minutes.
- Enhances customer experience with accurate availability.
Cons:
- Initial setup costs for cameras and software.
- Privacy concerns if not handled transparently.
- Requires good lighting for accuracy.
For best tools, check out solutions like Trax or IBM Watson Visual Recognition .
2. Healthcare Diagnostics
Computer vision analyzes medical images like X-rays or MRIs, spotting anomalies faster than docs alone. It’s a lifesaver in early detection of diseases like cancer. Google’s DeepMind, for instance, aids in eye disease diagnosis with superhuman precision.
A colleague in med-tech shared how it caught a tumor in a scan that was missed manually—talk about emotional impact. It doesn’t replace doctors but amps up their accuracy, especially in understaffed areas.
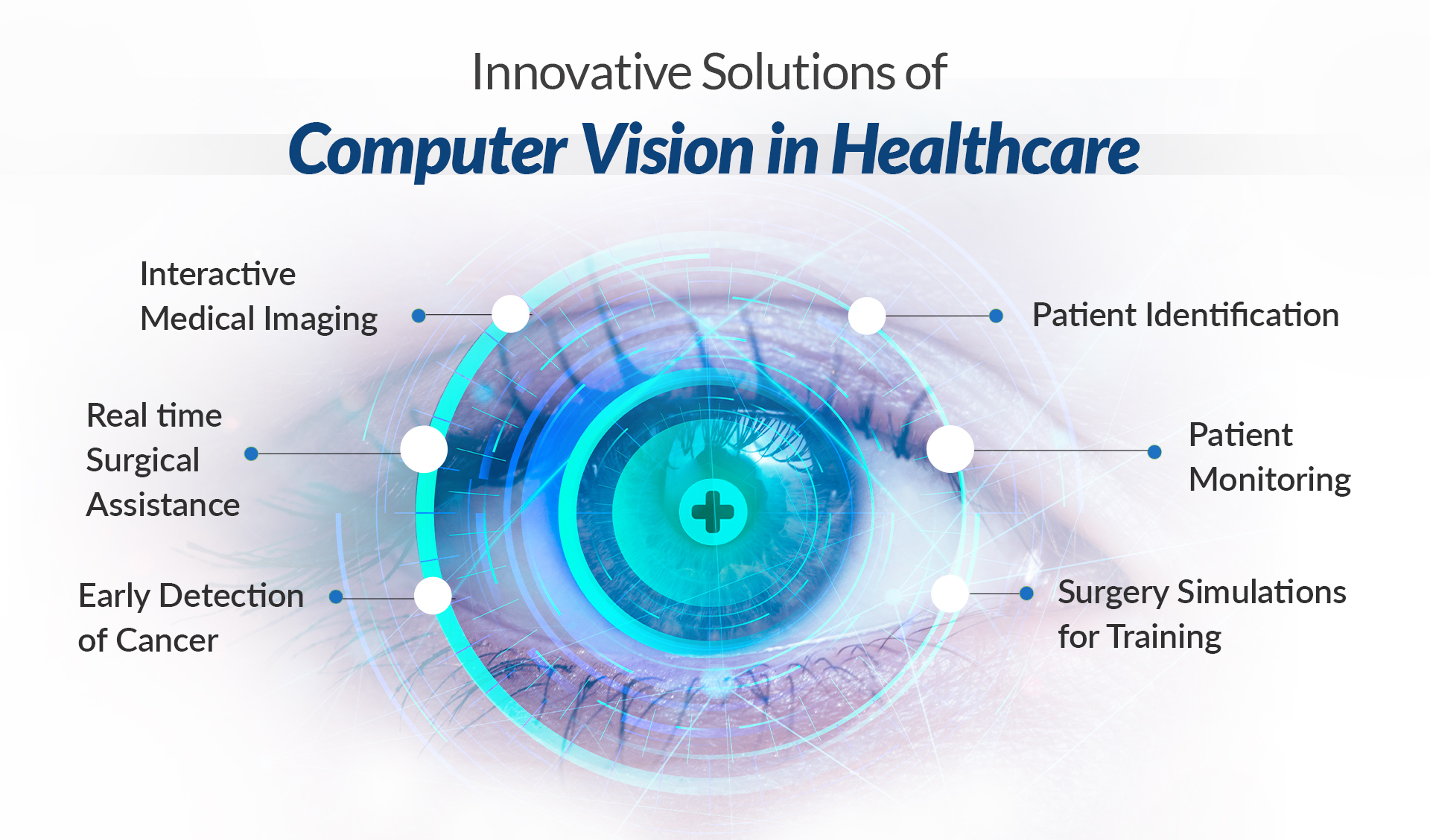
Computer Vision in Healthcare: How It is Transforming the Industry?
Pros:
- Improves diagnostic speed by 40-50%.
- Lowers error rates in image interpretation.
- Enables remote consultations in rural spots.
Cons:
- High data privacy risks under HIPAA.
- Needs massive datasets for training.
- Potential for biases if training data’s skewed.
Where to get started? Platforms like PathAI or Siemens Healthineers offer ready integrations .
3. Autonomous Vehicles in Automotive
Here, computer vision processes camera feeds to detect roads, pedestrians, and obstacles, enabling self-driving cars. Tesla’s Autopilot relies heavily on this, navigating traffic with real-time decisions.
I’ve ridden in prototypes, and it’s thrilling yet nerve-wracking—seeing the system dodge a sudden cyclist felt like sci-fi. It cuts accidents and could reshape logistics for businesses like Uber or FedEx.

Computer vision challenges in autonomous vehicles: The future of AI | SuperAnnotate
Pros:
- Reduces human error, potentially saving lives.
- Optimizes fleet management for lower fuel use.
- Opens doors to new services like robotaxis.
Cons:
- Vulnerable to bad weather or lighting.
- Regulatory hurdles slow rollout.
- Ethical dilemmas in decision-making.
Best tools include Waymo’s tech or open-source like Apollo from Baidu .
4. Manufacturing Quality Control
Cameras inspect products on assembly lines, flagging defects like scratches or misalignments instantly. Companies like Foxconn use it to ensure gadget perfection.
In a factory visit, I watched it reject flawed circuit boards—saved thousands in recalls. It’s tireless, spotting issues humans might miss after long shifts.
Computer Vision for Quality Control | softengi.com Сomputer Vision
Pros:
- Boosts defect detection accuracy to 99%.
- Speeds production without halts.
- Cuts waste and rework costs.
Cons:
- Upfront investment in high-res cameras.
- Integration with existing lines can be tricky.
- Over-reliance might skip subtle flaws.
Tools like Cognex or Keyence systems are top picks .
5. Agriculture Crop Monitoring
Drones with computer vision survey fields, detecting pests, nutrient lacks, or irrigation needs via image analysis. John Deere’s tech helps farmers optimize yields.
A farmer friend used it during a drought—spotted dry patches early, saving his crop. It’s eco-friendly too, reducing chemical overuse.

Computer Vision Application in Agriculture| Encord
Pros:
- Increases yields by 10-15% through precision.
- Lowers resource waste like water and fertilizers.
- Enables large-scale monitoring affordably.
Cons:
- Drones need skilled operators.
- Data overload without good analytics.
- Weather can affect drone flights.
Where to source? Blue River Technology or DJI Agri drones .
6. Security and Surveillance
Facial recognition and object detection enhance security, identifying threats or unauthorized access. Airports like those in Singapore use it for seamless checks.
I’ve seen it in action at events—caught a pickpocket mid-act, adding that wow factor. For businesses, it means safer premises and quicker responses.

Real-Time Face Recognition: Privacy Concerns and Biometric Security using Computer Vision | by Yuvarajharish | Medium
Pros:
- Real-time alerts prevent incidents.
- Integrates with access control systems.
- Scales for large areas like malls.
Cons:
- Privacy debates and potential misuse.
- Accuracy dips with masks or angles.
- High false positives in crowds.
Leading options: Verkada cameras or NEC’s NeoFace .
Comparing the 6 Applications
To help you pick what’s right for your biz, here’s a quick table breaking down key factors.
| Application | Industry Fit | Cost to Implement | ROI Timeline | Key Challenge |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Retail Inventory | Retail/E-commerce | Medium | 6-12 months | Lighting variability |
| Healthcare Diagnostics | Healthcare | High | 12-24 months | Data privacy |
| Autonomous Vehicles | Automotive/Logistics | Very High | 24+ months | Regulations |
| Manufacturing Quality | Manufacturing | Medium | 3-6 months | Integration |
| Agriculture Monitoring | Agriculture | Low-Medium | 6-12 months | Weather dependency |
| Security Surveillance | Security/All | Medium | 6-12 months | Ethical concerns |
This comparison shows manufacturing often delivers quickest wins, while autos demand patience but big payoffs.
Pros and Cons of Computer Vision Overall
Weighing it all? Here’s a balanced view.
Pros:
- Automates tedious tasks, freeing humans for creative work.
- Data-driven insights lead to smarter decisions.
- Scalable across business sizes with cloud options.
- Enhances safety in risky environments.
Cons:
- Requires quality data to avoid garbage-in-garbage-out.
- Upfront tech investment can sting for small firms.
- Ethical issues like bias need proactive fixes.
- Dependency on power and connectivity.
People Also Ask
Drawing from Google searches, here are real questions folks ask about this topic.
What are the main applications of computer vision in business? From retail to healthcare, it handles inventory, diagnostics, and more—boosting efficiency across boards.
How is computer vision used in retail? It tracks stock, analyzes customer behavior, and powers virtual try-ons for better shopping experiences.
What is an example of computer vision in manufacturing? Defect detection on lines, like spotting cracks in parts to ensure quality.
Is computer vision part of AI? Yes, it’s a subset using machine learning to interpret visuals.
Where can I learn more about computer vision tools? Sites like Coursera offer courses, or check vendors like Viso.ai for demos .
Best Tools for Getting Started
On the transactional side, here’s where to grab top tools. For beginners, try free tiers of Google Cloud Vision or Microsoft Azure Computer Vision. Mid-level? IBM Watson or AWS Rekognition. For enterprise, custom solutions from companies like Intellias . Head to their sites for trials—I’ve tested a few, and Azure’s user-friendly for quick prototypes.
FAQ
What skills do I need to implement computer vision in my business? Basic programming knowledge helps, but no-code platforms make it accessible. Partner with experts if you’re not tech-savvy.
How much does computer vision software cost? Starts at $0 for open-source like OpenCV, up to $10,000+ for enterprise setups. Cloud options bill per use, often pennies per image.
Is computer vision secure for business use? Yes, with encryption and compliance, but always audit for biases. Tools like those from Veritone prioritize security .
Can small businesses afford computer vision? Absolutely—affordable cameras and apps like those from AlwaysAI let you start small .
What’s the future of computer vision in business? Expect more edge computing for real-time processing and integration with AR. It’s evolving fast, per recent advancements [post:22].
Wrapping Up
So there you have it—the six powerhouse ways computer vision is fueling business growth. From my retail rescue story to global giants like Tesla, it’s clear this tech isn’t just futuristic; it’s here, solving real problems. If you’re pondering adoption, start small, test waters, and watch the efficiencies roll in. Got questions? Dive deeper with resources like Bernard Marr’s insights . Here’s to smarter, vision-powered businesses—cheers!
